LevelLoad
Deployment Transportation Scheduler or Replenishment Transportation Scheduler
Ensures deployment plans respect supply chain constraints, such as when a warehouse has limited space.
Patented Optimization System
LevelLoad uses a combination of linear programming and reinforcement learning to create more efficient schedules across a transportation network.

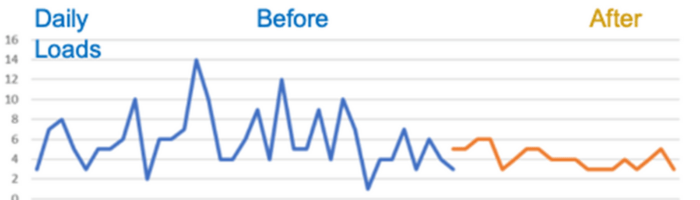
Smooth operations with LevelLoad
- Ensures deployment plans respect supply chain constraints such as when a warehouse has limited space
- Dramatic transportation cost reduction
- Improved on-time, in-full, delighting your customers.
Gartner Calls LevelLoad: a Deployment Transportation Scheduler
Ensures deployment plans respect supply chain constraints, such as when a warehouse has limited space.
- Dramatic transportation cost reduction
- Improved on-time, in full, delighting your customers.

LevelLoad FAQ
Does LevelLoad Replace Existing Supply Planning Solutions?
What Does LevelLoad Output?
Determines the number of trucks required on each lane each day for the next 30 days.
What Data Does LevelLoad Need To Operate?
LevelLoad uses data from your ERP or supply planning system:
- What is needed and its priority
- Production
- Forecast forecasts
At the same time the ERP and TMS provide:
- Existing customer orders and stock transfer orders
- Transportation rates and current capacities
- Current inventories
LevelLoad stores customer input data for:
- Parameters, such as how early or late certain items can be pulled
- Site space constraints
LevelLoad can integrate with most common ERP systems, and also provides an API interface.
How Configurable Is LevelLoad?
LevelLoad’s automated optimization engine is configurable – this includes optimization horizons, commit-to-load windows, and similar parameters. Transportation demand and constraint information is uploaded continuously and does not need to be entered manually.
What Is The Difference Between LevelLoad And Transportation Forecasting?
Transportation forecasting suggests what trucks will be needed while LevelLoad actually triggers tendering shipments. More importantly, working within user-set constraints, LevelLoad smooths demand out over the next month(s).
How Is Customer Service Maintained?
Customer service is improved by ensuring that higher priority items are still replenished prior to when their needed. This means that in many cases, inventory is delivered early. We ensure this occurs by creating placeholder stock transfers that are filled by stock priority much closer to shipment date using the latest available supply planning data. This data is often based on actual orders so priorities reflect what is truly needed rather than forecast days or weeks ago.
Why is it necessary to solve the whole network simultaneously?
Adjusting volume on any lane or site impacts other sites. Its like squeezing a balloon –so it is necessary to manage all the moves and capacities simultaneously
Why Can't Supply Planning Systems Level Transportation?
Planning systems may not have the load building capabilities or the ability to smooth shipments in an optimal way considering all constraints. LevelLoad complements these well as an add-on technology.
How Does LevelLoad Calculate Capacity At The Destination?
To calculate the available load capacity at a customer-facing DC, LevelLoad considers the customer sales orders that are already in-house as well as un-consumed forecast. These are netted against total available capacity, and then LevelLoad plans smoothed replenishment loads to each DC based on those daily net capacities, supply site capacities, and the specific transit days from each supply site.
When Does Levelload Run? How Long Does It Take?
LevelLoad normally runs overnight — immediately after a deployment (supply planning) system run. However, Levelload can run at any desired schedule. Very large networks take around 15 minutes to solve.
How Does LevelLoad Know How Much Product Will Fit Into A Given Number Of Loads?
As it solves, LevelLoad uses its own 3D load builder to estimate which products will fit on a given number of loads on a given day. These estimates are used only to help decide on the best number of placeholder loads on each lane each day. Later, a load building solution is used to turn placeholders loads into actual loads based on SKU priorities at that point in time.
What Hard And Soft Constraints Can LevelLoad Handle?
Levelload can handle constraints including:
- carrier capacity by lane and day
- location ship and receive capacity by lane and day
- location storage capacity by day
- transit times by carrier and day
- cost
- priority
- and more.
These constraints can be hard or “flexible”. A flexible constraint recognizes that there may be wiggle-room – a site may only be able to ship and receive 100 loads, but by paying overtime, additional shipping capacity is generated.